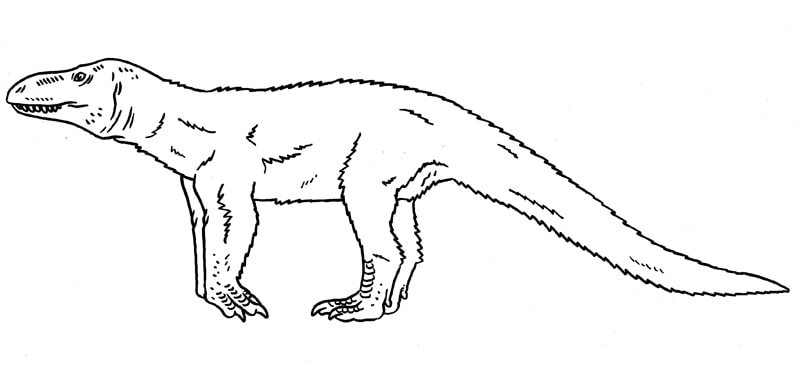
Mesozoic
Triassic
A relative of Rebellatrix that evolved a shape and size similar to that of later icthyosaurs. Rebellatricidae
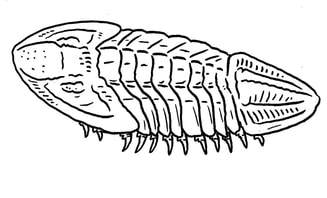
Relictual, deep sea trilobite that survived the great dying. Proteida.
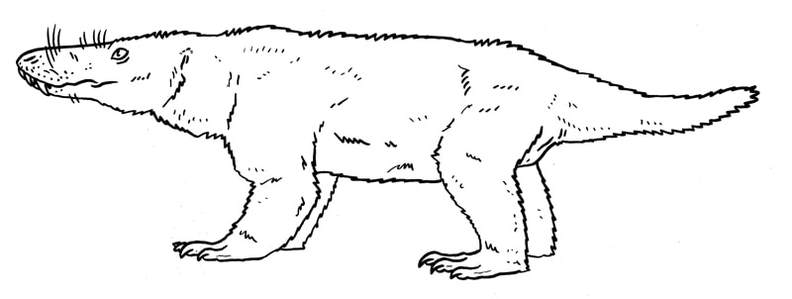
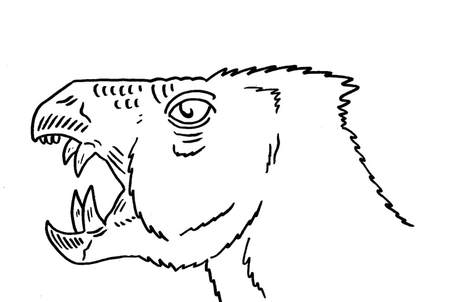
A therocephalian which has convergently evolved live birth, of well developed young. Ericiolacertidae.
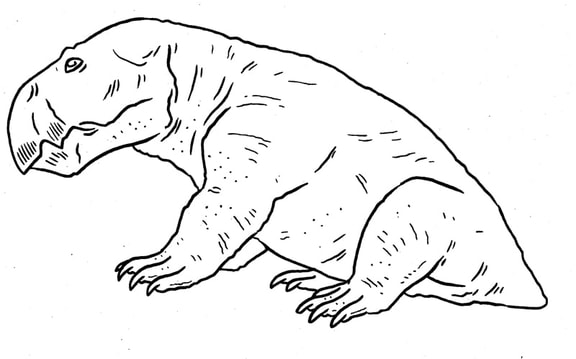
A Triassic Dicynodont that feeds exclusively on one kind of tough-plant, much like a panda. Dicynodontia.
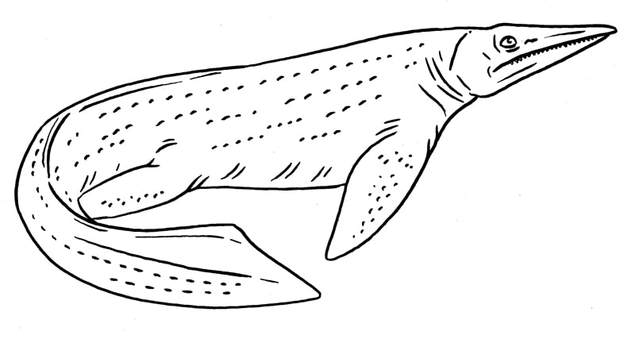
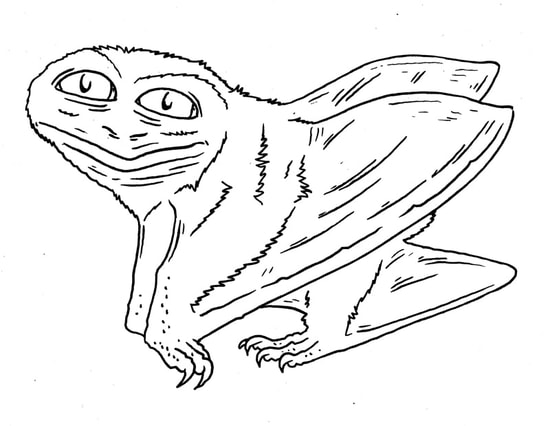
A relative of Cartorhychus, which has re-adapted to a primarily terrestrial existence. Stem Ichthyosauria.
A larger relative of Qianosuchus, about 6 meters long. Poposauroidea.
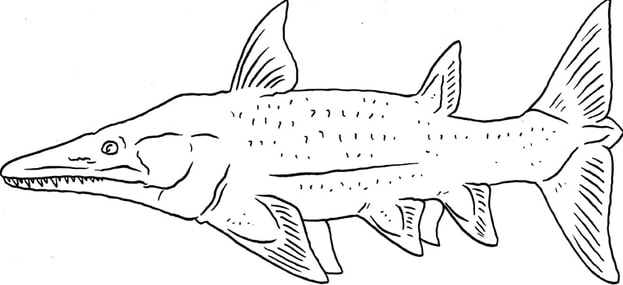
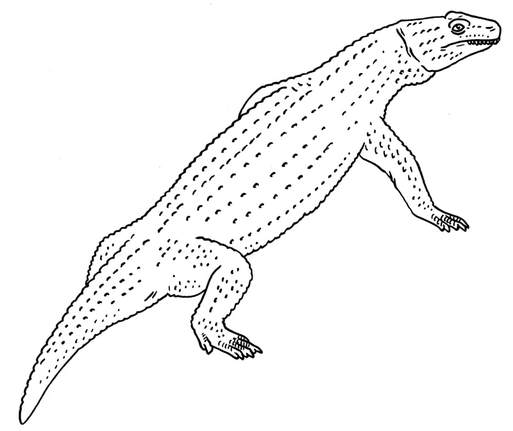
A fair-sized primitive ichthyosaur, which can haul out on land like a sea lion. Stem Ichthyosauria.
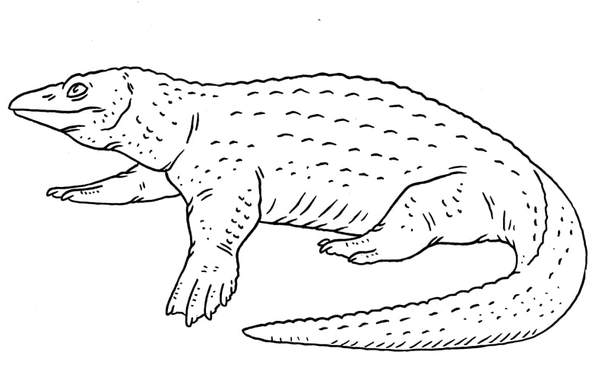
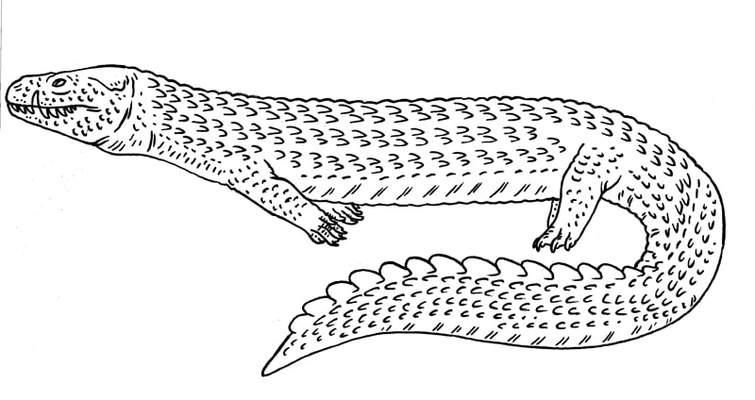
An ancestral placodont which is terrestrial, having not yet developed aquatic habits. Placodontia.
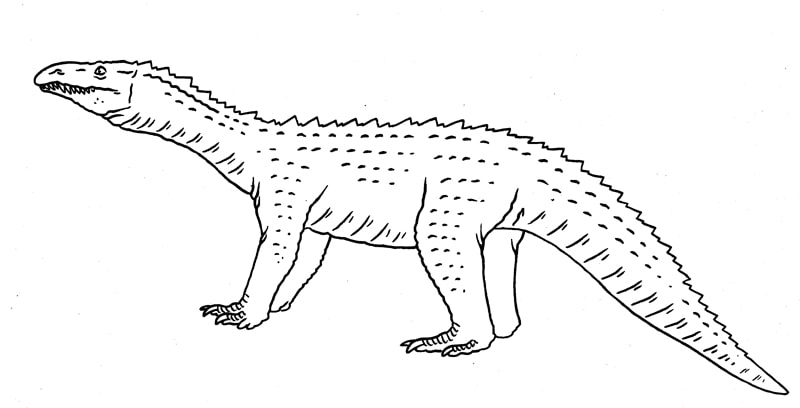
A small, wide-bodied aetosaur. Stagonolepididae.
An oversized relative of Vanclavaea, perhaps 3.5 meters long. Archosauriformes.
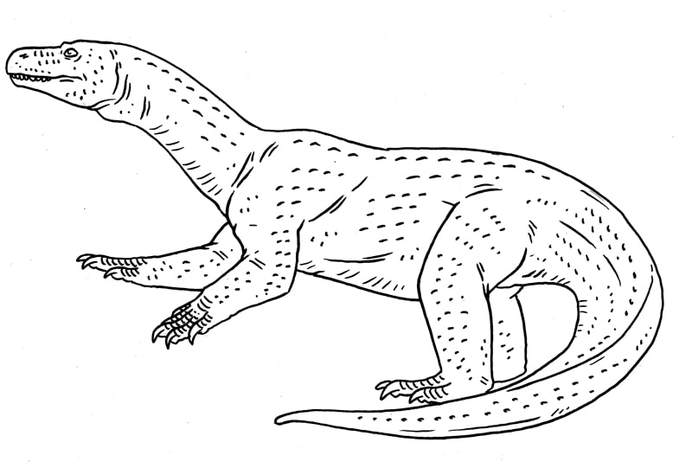
A relative of Azendohsaurus which reaches a large size of about 4.5 meters, and can stand and walk on its hind legs. Vaguely resembling a prosauropod. Allokotosauria.
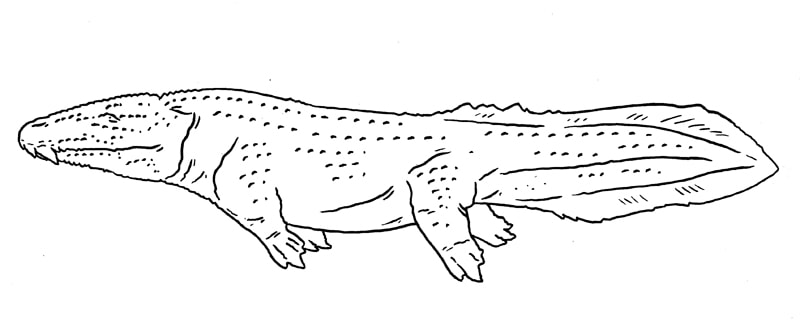
A labyrinthodont that is adapted to catch prey in very murky water, hence being blind. Stereospondyli.
A species of hybodont that feeds like a cookiecutter shark, by taking chunks off marine reptiles and large fish. Hybodontiformes novis.
Jurassic
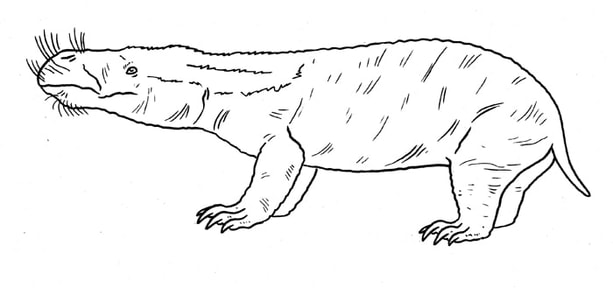
A burrowing subterranean Tritylodont that resembles a naked mole rat in some ways. Tritylodontidae.
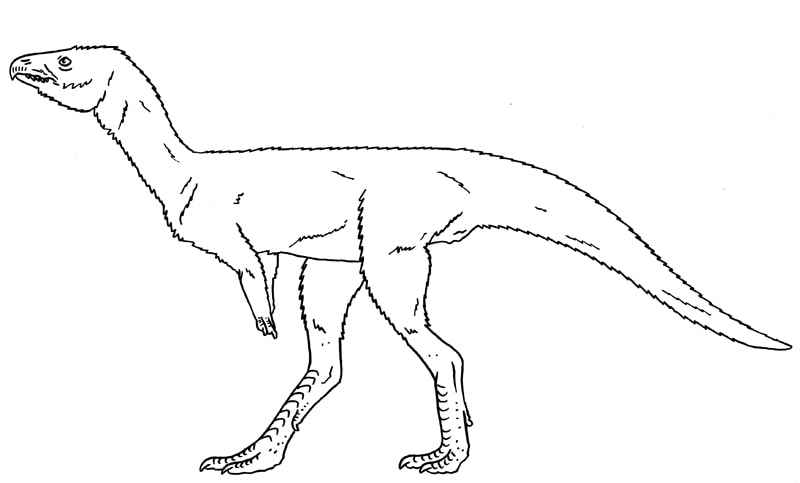
A carnivorous heterodontosaur. Heterodontosauridae.
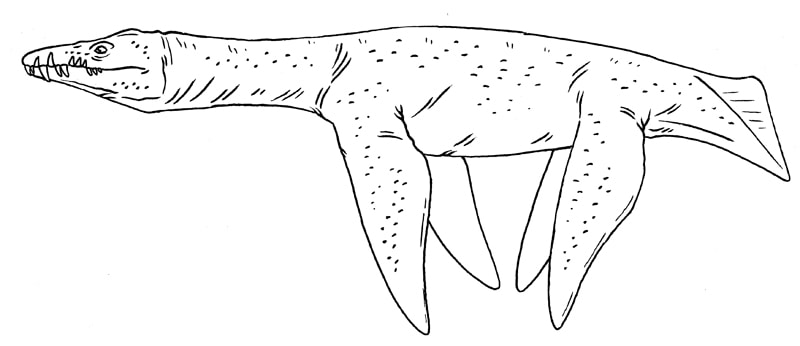
A Rhomaleosaur that combines large, pliosaur-like fangs with a relatively long neck. Rhomaleosauridae.
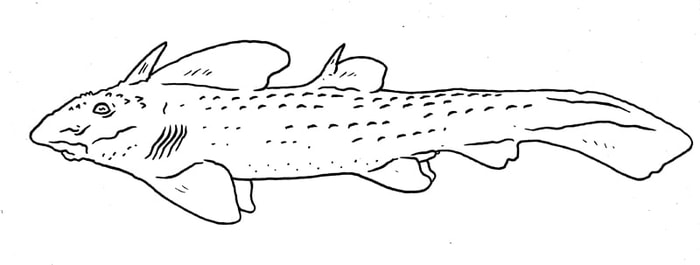
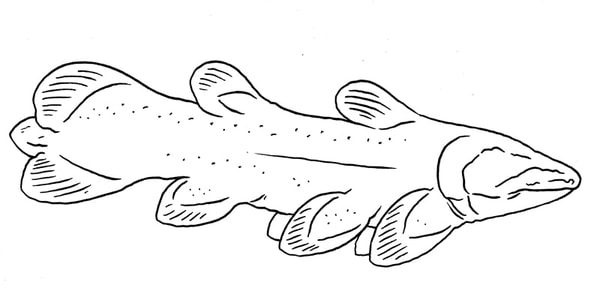
A cave-dwelling kind of coelacanth, being blind and colorless. Latimerioidei novis.
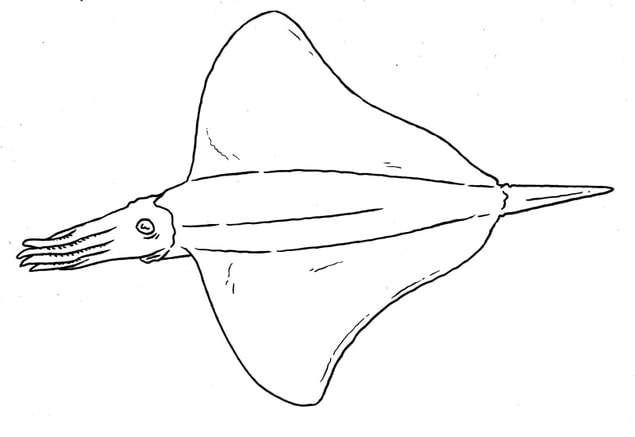
A species of belemnite whose fins resemble a ray or skate in their extent. Belemnoidea.
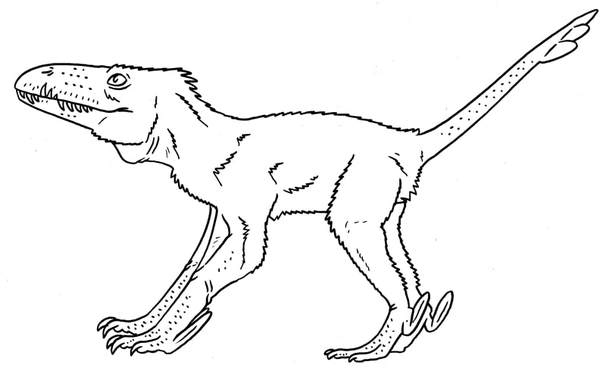
A partially quadrupedal relative of tetanurans. Stem Tetanurae.
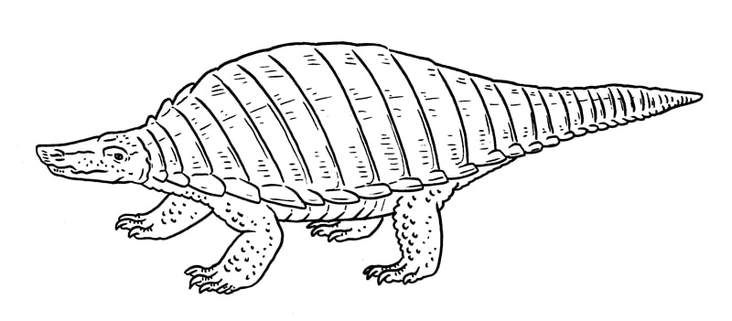
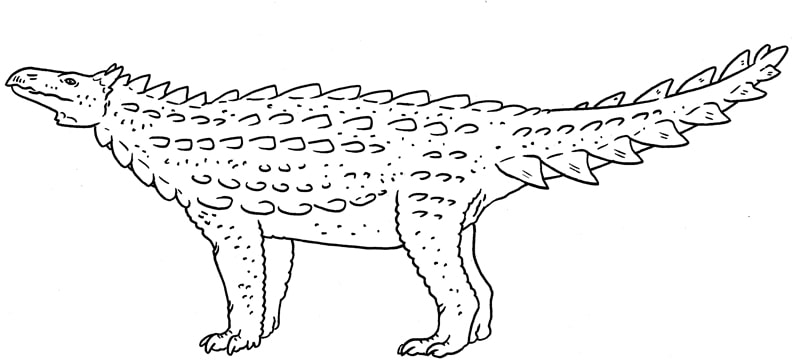
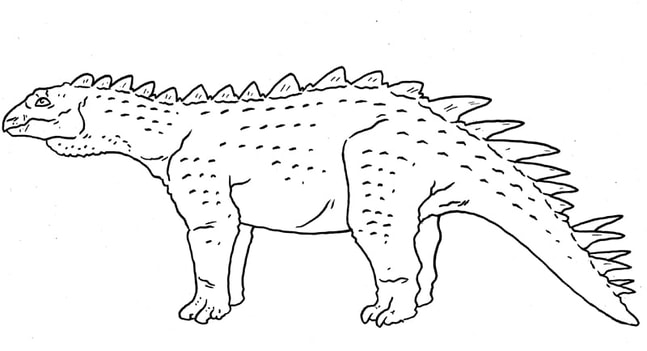
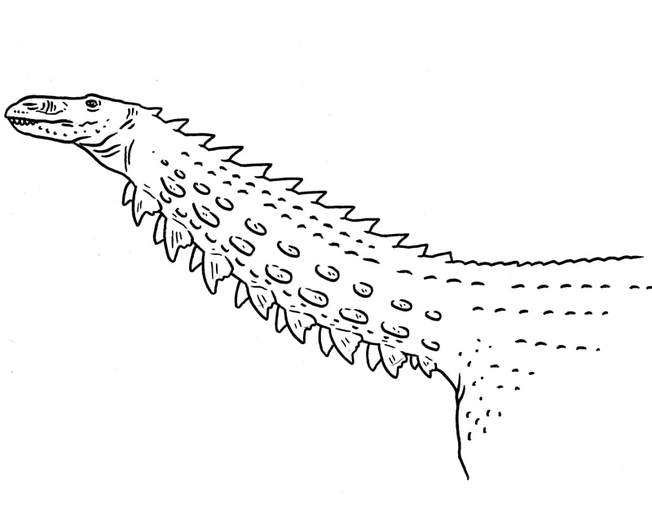
A relative of Scelidosaurus which has blade-like tail armour similar to Gastonia. Scelidosauridae.
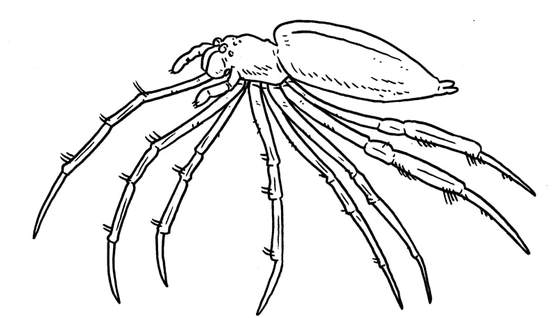
A giant orb-weaving spider that is able to catch small pterosaurs and juvenile dinosaurs. Nephilinae.
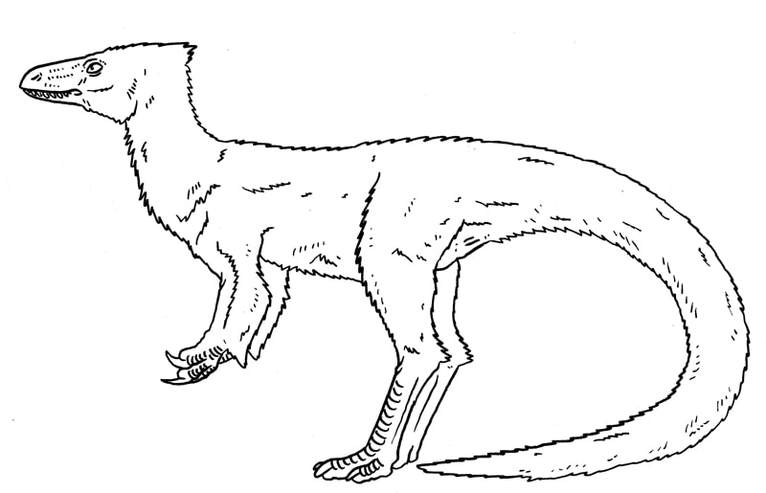
A carnivorous relative of Limusaurus, that is adapted to catch small vertebrates and insects. Elaphrosaurinae.
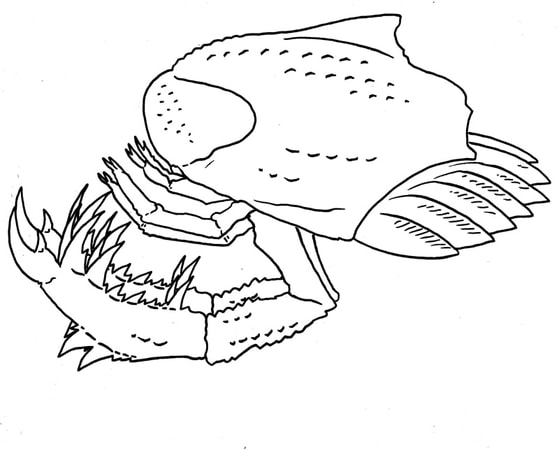
A relative of Dollocaris that reaches a large size, carapace about as big as a fist. Concavicarida.
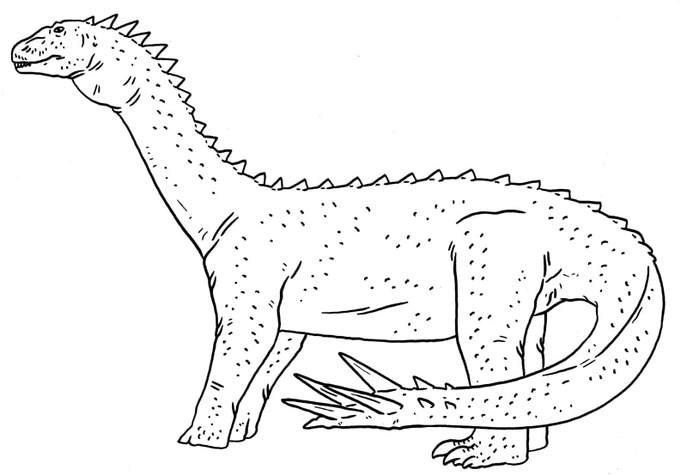
A Shunosaurus-like dinosaur, that has a large thagomizer instead of a tail club. Sauropoda.
A flightless, island-dwelling Dimorphodontid with only vestigial wings. Dimorphodontia.
A coelurid maniraptoran which is able to run in cheetah-like bursts of high speed, to catch its prey. Coeluridae.
An insular stegosaur that has existed without significant predators, hence its spines are smaller. Dacentrurinae.
An Apatosaurus-like dinosaur which has large, ossified spikes and armour on its neck. Apatosaurinae.
A relative of Anurognathus that feeds by pouncing on terrestrial vertebrates, like an owl. Anurognathidae.
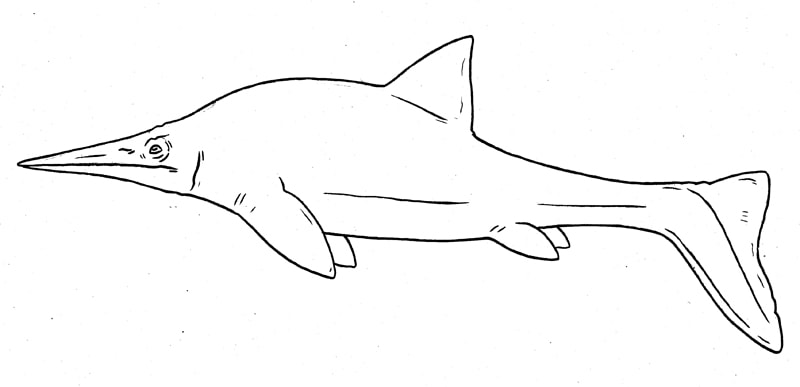
A freshwater ichthyosaur. Stenopterygiidae.